Navigating Global Trade: An Overview of the Export Business
The export business, a cornerstone of global commerce, has a history as old as trade itself. From the ancient Silk Road facilitating the exchange of goods between East and West, to the maritime trade routes that connected continents, the movement of products across borders has shaped economies and cultures. Modern export practices, however, have evolved significantly, driven by technological advancements, globalization, and shifting consumer demands. The 20th and 21st centuries witnessed the rise of multinational corporations, complex supply chains, and digital platforms that have revolutionized how goods and services are traded internationally. Today, the export business is characterized by a dynamic interplay of economic, political, and social factors, requiring businesses to be agile and adaptable to thrive in a competitive global marketplace.
Current trends in the export business are heavily influenced by digital transformation and sustainability. E-commerce platforms have democratized access to international markets, enabling even small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to reach global customers. The rise of digital marketing, social media, and online marketplaces has streamlined the process of identifying potential buyers and facilitating transactions. Furthermore, there’s a growing emphasis on sustainable and ethical trade practices, with consumers increasingly demanding products that are environmentally friendly and socially responsible. Businesses are responding by adopting greener production methods, implementing fair labor practices, and engaging in circular economy initiatives. The focus on supply chain resilience, highlighted by recent global disruptions, is also driving companies to diversify their sourcing and distribution networks to mitigate risks.
Despite its vast potential, the export business presents numerous challenges. Navigating complex regulatory frameworks, including customs procedures, tariffs, and trade agreements, can be daunting for businesses, especially SMEs. Currency fluctuations and political instability in certain regions can also create significant uncertainties and financial risks. Moreover, cultural differences and language barriers can hinder effective communication and business negotiations. Competition from established players and the need to maintain competitive pricing while ensuring quality are constant pressures. Building strong relationships with international partners and distributors requires time, resources, and cultural sensitivity. Ensuring compliance with international standards and certifications adds another layer of complexity.
The scope of the export business is vast, encompassing a wide range of industries and sectors. From agricultural products and manufactured goods to digital services and intellectual property, the potential for international trade is immense. Emerging markets in Asia, Africa, and Latin America offer significant growth opportunities for businesses seeking to expand their reach. The increasing demand for specialized products and services, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences, creates new avenues for innovation and export diversification. The rise of the digital economy has also opened up new possibilities for cross-border trade in services, including software development, online education, and digital marketing. The future of the export business lies in embracing innovation, adapting to changing market dynamics, and fostering sustainable and inclusive trade practices.
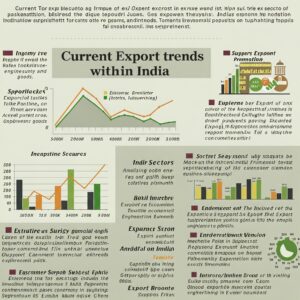
The Indian government has implemented several initiatives to promote exports and support businesses in their international endeavors.
Schemes like the Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS) and the Services Exports from India Scheme (SEIS) provide incentives to exporters across various sectors.The “Make in India” initiative encourages domestic manufacturing and promotes exports of Indian-made products.The government has also focused on streamlining customs procedures, reducing transaction costs, and improving infrastructure to facilitate trade.The Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) plays a crucial role in formulating and implementing trade policies and providing guidance to exporters.Furthermore, the government actively participates in international trade negotiations to secure favorable market access for Indian products and services.By fostering a conducive environment for exports, the Indian government aims to boost economic growth, create employment opportunities, and enhance the country’s competitiveness in the global marketplace.